The maintainer isn't answering issues or making changes at: github.com/PeterHughes/SharpChess
Therefore you may want to try piplay's fork with fixes for cross-platform issues and with some other improvements.
Below is from the original codeproject.com post.
![]()
4.93/5 (313 votes)
5 removed
updated 25 Oct 2020
12 min read
SrcChess SharpChess is a chess program built in C#
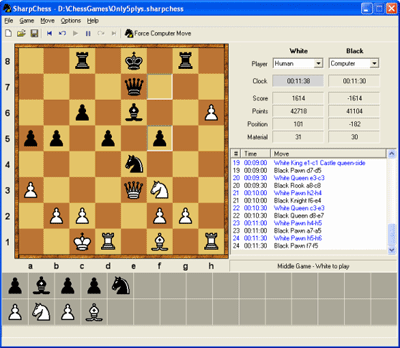
SrcChessSharpChess is a chess program built in C#. Although it is not on par with commercial chess programs, SrcChessSharpChess is beating me without any problem and therefore can be a serious opponent for casual players. The program supports a reasonable number of functions. Its biggest weaknesses are probably the lack of a good board evaluation function and of an end game database. One of its strengths is that it takes advantage of multiple processors when available. The program also includes a PGN filter that lets you import games in PGN format and build your own openings book.
I decided to make my program available so programmers can understand how a chess program works. I also hope some people will improve it.
This chess program features:
Version 3.0
Version 2.05
Version 2.04
Version 2.03
Version 2.02
Version 2.01
Version 2.00
Version 1.10
<font face="Courier New">System.Threading.Tasks </font>to simplify the multi-threading implementation<font face="Courier New">ChessControl</font>Version 1.00
Version 0.943.000
Version 0.942.000
Version 0.941.000
Version 0.940.000
Version 0.930.002
Version 0.930.001
The program is developed in C# using Visual Studio 2010. It uses the alpha-beta pruning search algorithm (and minimax for debugging) to search for the next best move. To decrease the number of moves to evaluate, the search algorithm uses a transposition table implemented with Zobrist hashing.
To further improve the performance of the search, the program uses one thread per processor found on the computer and splits the search among them (finally a use for the multiple processors on my computer...). The search threads are low priority so as not to disturb too much the computer response.
The program uses a database of book openings. The one provided with the game was built from PGN files. The program also provides a PGN parser so you can build your own openings database using an option on the Tool menu. The parser also allows you to replay chess games downloaded from the Web in PGN format.
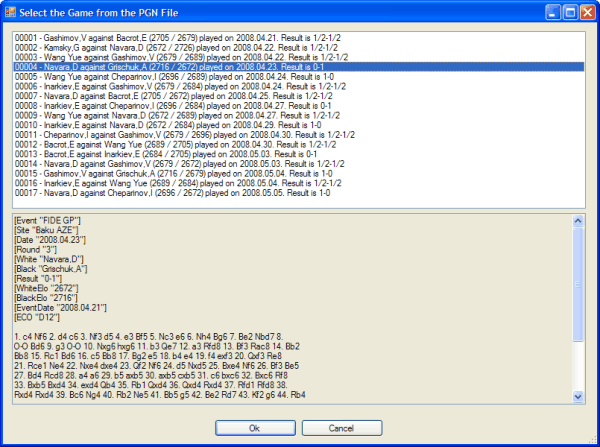
A database of book openings is provided with the program. You can build your own openings book from any PGN file (easily found on the Web).
The program includes a parser that allows you to import and filter the content of a PGN file according to parameters such as players or rankings. This filtered version of the PGN file can also be saved and used to create an openings book.
The openings book must be located in the directory containing the executable and named book.bin.
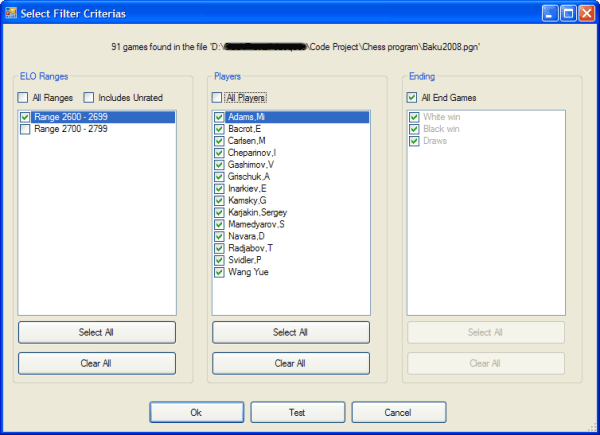
The board evaluation function is minimalist. Improvements on this function will greatly enhance the level of playing of the program. Similarly, the end game stage of the program could benefit from the inclusion of an end game database.
There is no rating among the different openings; an opening is thus chosen randomly.
Improvements can also be made on the user interface. Adding a help file to the game would be welcome.
A chess program is not very complex in itself. But like a lot of software, the devil is in the details. This chess program contains around 10,000 lines of codes (including remarks). The user interface is separated from the other classes so it can easily be changed.
The ChessBoard class is the most important since it contains the board abstraction. It also contains the logic to build the list of legal moves and to search for the best move. A little extra complexity was added to support multi-threading. However, the class is relatively small (less than 2000 lines). To improve the speed of the search, a list of legal moves for each {piece, piece position} is created once in the static constructor of the class.
ChessBoard: Class constructorCopyFrom: Copy a board into another oneClone: Create a clone of the boardReadBook: Read an openings book from a fileSaveBoard: Save the board to a streamLoadBoard: Load the board to a streamResetBoard: Reset the board to initial positionthis[int iPos]: Default indexer, get or set a piece on the boardGetEatedPieceCount: Return the number of pieces which have been captured for a given colorDoMove: Do the specified moveUndoMove: Undo the specified moveWhitePieceCount: Number of white pieces on the boardBlackPieceCount: Number of black pieces on the boardIsCheck: Determine if a given color king is being directly attackedEnumMoveList: Enumerate all the possible moves for a given colorFindBestMove: Find the best move for a given color using alpha-beta or minimaxFindBookMove: Find a move in the openings bookGetHumanPos: Return a human readable move from a move structureCancelPlay: Cancel the background searchThe core logic of the search lies in the alpha-beta pruning function. This function can be used in two modes:
The first method searches for the best move in a specified number of ply.
The second one tries to find the best move in a specific amount of time using an iterative depth-first search, increasing the number of ply for each search up to the moment when time is exhausted. At first glance, this method may seem less efficient since it performs the same search repeatedly. But in practice, the method reorders the moves between each search to optimize the alpha-beta cut-off. Another big advantage of this method is that the number of ply can be adjusted depending on the stage of the game. In particular, the end game holds fewer pieces on the board, so increasing the number of ply doesn't have the same impact as doing so in the middle of the game.
The following lists the source files and description. The number of lines appears in brackets after the name of the file. The code has a total of 9836 lines.
Assembly.cs (34) Assembly file for .NET application.
Book.cs (359) Implements the book openings.
ChessBoard.cs (1990) Implements the chess board regardless of the user interface. This is where the core logic of the program lies (search, legal moves, etc.). The search function is implemented using minimax and alpha-beta algorithms, using multi-threading when possible.
ChessControl.cs (1510) User interface for the chess board. Implemented as a UserControl.
ChessControl.Designer.cs (86) Visual Studio generated code for the control.
frmAbout.cs (16) About dialog box.
frmAbout.Designer.cs (110) Visual Studio generated code for the form.
frmChessBoard.cs (1236) Main form containing all the other controls (ChessControl, MoveViewer, etc.).
frmChessBoard.Designer.cs (499) Visual Studio generated code for form.
frmCreatePGNGame.cs (114) Interface to convert a PGN file into a book openings database.
frmCreatePGNGame.Designer.cs (97) Visual Studio generated code for the form.
frmGameParameter.cs (165) Parameters of the game.
frmGameParameter.Designer.cs (218) Visual Studio generated code for the form.
frmPGNFilter.cs (340) Parameters for filtering a PGN file.
frmPGNFilter.Designer.cs (309) Visual Studio generated code for the form.
frmPGNGamePicker.cs (209) Choosing from PGN game.
frmPGNGamePicker.Designer.cs (103) Visual Studio generated code for the form.
LostPiecesControl.cs (299) Control used to show the captured pieces.
LostPiecesControl.Designer.cs (63) Visual Studio generated code for the control.
MoveViewer.cs (192) Control used to show the moves.
MoveViewer.Designer.cs (87) Visual Studio generated code for the control.
PGNParser.cs (765) Parser for PGN notation.
PgnUtil.cs (816) Utility class for PGN files.
Program.cs (21) Main program.
TransTable.cs (232) Transposition table implementation.
All terms can be easily found on the Web (Wikipedia is a good source).
A ply consists of a half move (a move of one side only). A 4-ply search means to search 2 moves in advance.
Portable Game Notation, or PGN, is a notation used to record chess games. PGN is widely used as it is easy to read by users and to process by computers. Many chess games and events are published in the PGN format. The parser allows the chess program to read these files.
Minimax is a recursive algorithm use for choosing the next move in a game. A tree of legal moves is built and played. Each move is evaluated using an evaluation function. The computer makes the move that maximizes the minimum value of the position resulting from the opponent's possible following moves.
The alpha-beta pruning function is an improvement of the minimax search method. It reduces the number of nodes to evaluate by eliminating a move when at least one possibility was proved worse than a previously evaluated one.
A transposition table is a hashing table that records the previous moves' evaluations so they will not have to be re-evaluated. Transposition tables are used to speed up the search of the game tree. They are implemented using Zobrist hashing .
To implement a transposition table, it is important to determine if two boards are equivalent in configuration and in potential moves. To do so, we can just compare the pieces of the two boards, but we must also take into account castling and en-passant moves, as they constrain possible moves. The only problem is that this method is a quite long when considering it has to be used millions of times to evaluate each move. Zobrist hashing simplifies this process by assigning each board position a 64-bit signature; instead of checking each piece one by one to see if the board has already been evaluated, we just compare the two 64-bit values.
This article, along with any associated source code and files, is licensed under The GNU General Public License (GPLv3)
![]()
Team Leader Consyst SQL
Watch
this Member
Have the articles and posts from this member appear in your Timeline so you can stay up to date.
Unwatch
Stop following this Member
Canada 
Consyst is a dynamic IT company specialized for more than 20 years in information technology architecture and in the development of innovative productivity tools for businesses. Rep++, the product at the core of its mission, can significantly accelerate the development cycle of applications and services by reducing the duration of the design, coding, testing and maintenance stages. Rep++ ...
Consyst is a dynamic IT company specialized for more than 20 years in information technology architecture and in the development of innovative productivity tools for businesses. Rep++, the product at the core of its mission, can significantly accelerate the development cycle of applications and services by reducing the duration of the design, coding, testing and maintenance stages. Rep++ uses a model-driven approach supported by a powerful model execution mechanism. Essential complement to Visual Studio® (Microsoft®), Rep++ includes: an open and centralized model that is used to define, contain and manage all the metadata of an application set; toolkits and application frameworks that implement various flavors of the presentation layer; and specialized assistants that simplify the creation of applications and services for a variety of architectures and technologies. These elements provide a very high automation level, which enable businesses to focus their development efforts on where it counts: their business rules.